

Maintaining oral health is a critical aspect of overall well-being. Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common condition that can lead to severe dental complications if not managed properly. In this guide, we will explore the importance of oral health, define gum disease, elaborate on its stages, and discuss risk factors as well as prevention and treatment options.
Oral health is an essential part of maintaining a healthy lifestyle. The condition of your teeth, gums, and mouth reflects not only your dental hygiene practices but also your overall health. Poor oral health can result in various complications, such as infections, tooth loss, and other systemic diseases. Neglecting oral health can lead to a cascade of issues, affecting not just the mouth but also the body as a whole. For instance, the presence of untreated cavities or gum disease can result in chronic pain, which may affect your ability to eat, speak, and even socialize comfortably.
Many people underestimate the consequences of neglecting oral health. Bacteria that thrive in the mouth during gum disease can enter the bloodstream, potentially leading to serious health issues, including heart disease and diabetes. The mouth serves as a gateway to the body, and maintaining its health is vital for preventing the entry of harmful pathogens. Therefore, understanding and investing in oral health is crucial for comprehensive well-being. Regular dental visits not only help in catching issues early but also provide an opportunity for education on proper oral care techniques, ensuring that individuals are well-equipped to take charge of their dental health.
Good oral hygiene is key to preventing gum disease. This involves regular brushing and flossing, along with yearly dental check-ups. Brushing at least twice a day helps remove plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that can lead to inflammation and infection if left unchecked. The choice of toothbrush and toothpaste can also play a significant role; using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste can enhance the effectiveness of your brushing routine.
In addition to brushing, flossing daily helps to clean areas between the teeth that toothbrushes cannot reach. Using antibacterial mouthwash can also contribute to oral hygiene by reducing plaque and fighting bacteria. These practices build a strong foundation to prevent gum disease and maintain healthy gums and teeth. Moreover, incorporating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can further support oral health, as nutrients like calcium and vitamin D are essential for maintaining strong teeth and bones. Keeping hydrated is another vital aspect, as saliva plays a crucial role in neutralizing acids and washing away food particles, thereby reducing the risk of decay.
Research indicates a strong link between gum disease and various systemic health conditions. For instance, individuals with periodontal disease are at a higher risk for heart disease, stroke, and respiratory conditions. The inflammation caused by gum disease may also exacerbate these health issues, creating a detrimental cycle. Furthermore, studies have shown that pregnant women with gum disease may experience complications such as premature birth and low birth weight, highlighting the importance of oral health during critical life stages.
Furthermore, conditions such as diabetes can lead to an increased risk of gum disease due to poorer blood flow and a compromised immune system. This makes it essential for individuals with chronic health conditions to maintain proper oral care and stay vigilant about their gum health. Regular monitoring of oral health can serve as an early warning system for other health issues, making it imperative for healthcare providers to integrate dental assessments into routine medical care. By fostering a holistic approach to health that includes oral hygiene, individuals can significantly enhance their quality of life and reduce the risk of developing serious health complications down the line.
Gum disease is an inflammatory condition affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. It is primarily caused by the accumulation of plaque—a film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. If not properly managed, plaque can harden into tartar, which can only be removed through professional dental cleaning. The presence of plaque not only contributes to gum disease but can also lead to other systemic health issues, as the bacteria can enter the bloodstream and affect various organs.
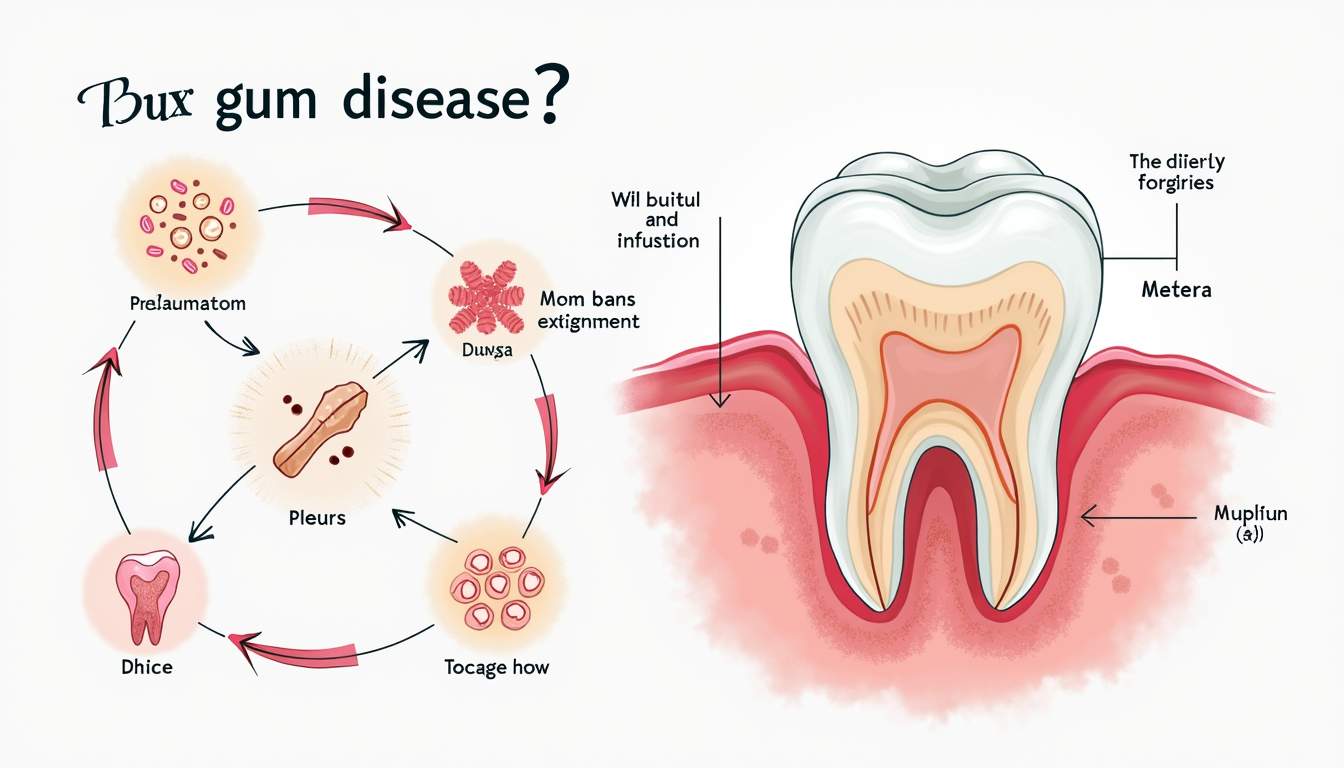
The progression of gum disease can lead to serious oral health problems if left untreated. Understanding its stages can help individuals identify early signs and symptoms, which is essential for effective treatment and prevention. Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing twice a day and flossing daily, are key components in combating gum disease and maintaining overall health.
Periodontal disease encompasses a range of inflammatory conditions that affect the supportive structures of the teeth, including gums, alveolar bone, cementum, and the periodontal ligament. It is commonly classified into two categories: gingivitis and periodontitis. The transition from gingivitis to periodontitis can occur without noticeable symptoms, making it crucial for individuals to stay vigilant about their oral health.
Gingivitis is the mildest form of gum disease, while periodontitis represents a more advanced stage where the gums pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that become infected. Left untreated, periodontitis can lead to significant tissue and bone loss, potentially resulting in tooth loss. Moreover, research suggests that periodontal disease may be linked to other health conditions, such as heart disease and diabetes, highlighting the importance of addressing gum health as part of overall wellness.
Recognizing the symptoms of gum disease is crucial for early intervention. Common signs include:
If you experience these symptoms, it is vital to schedule a dental appointment as soon as possible to evaluate the condition of your oral health. Additionally, individuals should be aware that certain risk factors, such as smoking, hormonal changes, and genetic predisposition, can increase the likelihood of developing gum disease. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can also support gum health, as nutrients like vitamin C play a vital role in tissue repair and immune function.
Gum disease typically progresses through three critical stages, each with its own characteristics and implications for oral health. Understanding these stages helps in identifying the condition early and seeking treatment timely.
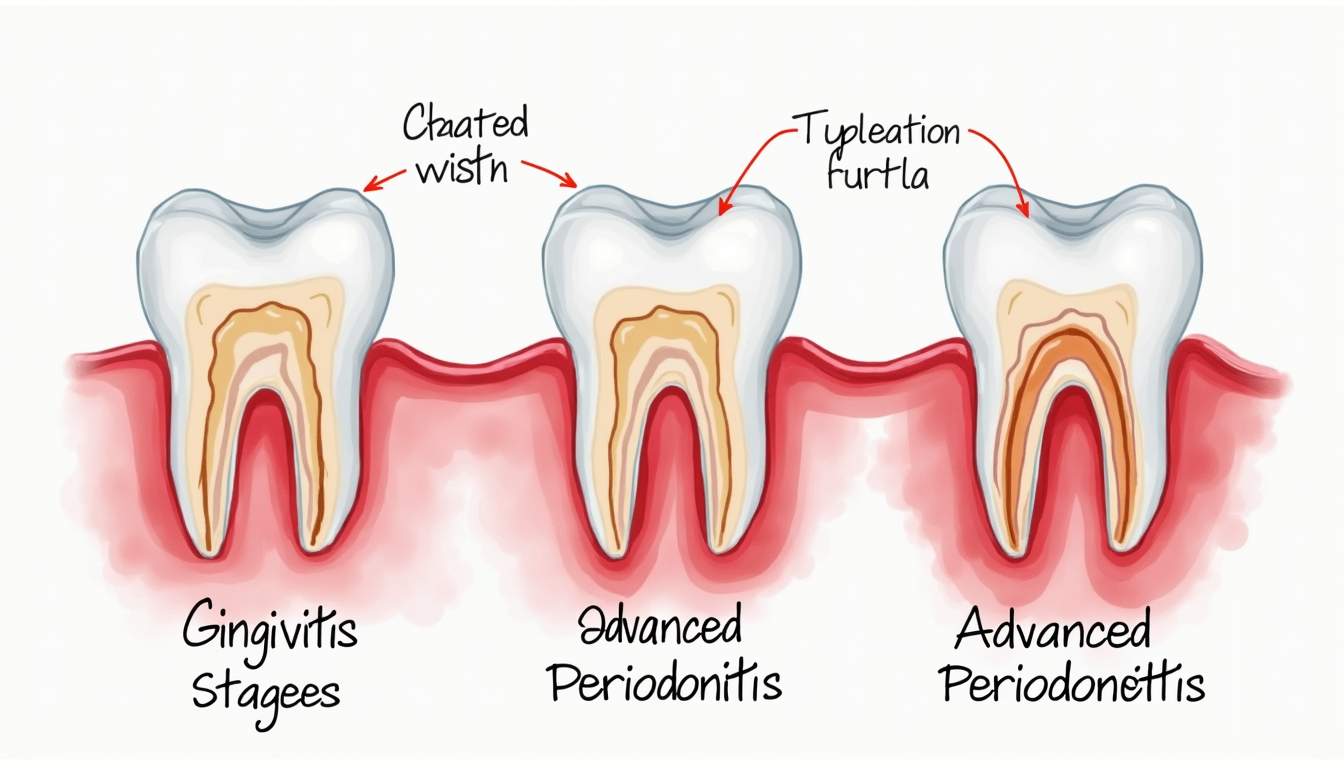
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease, marked by inflammation and irritation of the gums. This stage is often reversible with proper oral hygiene. Symptoms may include red, swollen gums that may bleed when brushing.
At this stage, plaque build-up can lead to gingivitis; however, if addressed through improved oral care, it can be reversed, preventing the progression to more damaging stages.
If gingivitis remains untreated, it can progress to periodontitis. The inflammation extends deeper into the supporting structures of the teeth, causing gum pockets to form. This is a more severe stage where the risk of losing teeth significantly increases if proper treatment is not pursued.
Your dentist may recommend professional cleanings more frequently, along with personalized dental care plans to manage this stage of gum disease effectively.
Advanced periodontitis is the most severe stage of gum disease, characterized by significant loss of gum tissue and supporting bone. Symptoms may include intense pain, tooth mobility, and pronounced gum recession.
At this point, tooth loss becomes a serious concern, necessitating extensive treatment options which may include surgical interventions or tooth replacement procedures. It is critical to act rapidly at this stage to salvage overall oral health.
Various risk factors contribute to the development of gum disease, emphasizing the need for attention to prevention and management strategies. Understanding these factors can provide insights into how to protect your oral health better.
Several lifestyle choices can increase the risk of developing gum disease. Poor diet, particularly one high in sugars and low in vitamins, can negatively impact gum health. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are also significant contributors, as they impair the immune system and reduce blood circulation to the gums.
Stress has been known to affect oral health as well, as it can lead to increased plaque build-up and decreased immune function. Managing these lifestyle factors is essential for preserving gum health.
Numerous medical conditions can predispose individuals to gum disease. Diabetes is one of the most notable, as uncontrolled blood sugar levels can impair the body’s ability to fight off infections, including those in the gums.
Other conditions such as autoimmune diseases, certain cancers, and medications that cause dry mouth also contribute to an increased risk. For this reason, discussing oral health with your healthcare provider is crucial for managing these risks effectively.
Effective prevention and treatment strategies for gum disease are vital. Staying informed and proactive can significantly reduce the risk of developing severe gum conditions and ensure a healthier mouth.
Establishing a consistent daily oral care routine is paramount. This includes brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily to remove plaque from hard-to-reach areas.
Furthermore, utilizing mouthwash that contains antibacterial properties can help inhibit plaque growth. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings every six months will fortify your efforts to maintain optimal gum health.
If gum disease is detected, various professional treatments are available, depending on the stage of the disease. These treatments may include scaling and root planing (a deep cleaning procedure), antibiotic therapies, or more advanced treatments such as gum surgery in severe cases.
It is crucial to follow your dentist’s recommendations and attend regular follow-up appointments to monitor progress and make adjustments as needed. Recognizing gum disease early and seeking timely treatment are key to preserving dental health and preventing complications.
Our office is proud to offer the latest in dental technologies to provide you with the best in-office experience.
Complete the form below and a staff member will be in touch with you shortly to schedule your appointment.